আজকে আমরা পাইথনের একটি অত্যন্ত গুরুত্বপূর্ণ ডেটা – স্ট্রাকচার, Dictionary নিয়ে বিশদে আলোচনা করব। এই পোস্টে আমরা জানব ডিকশনারি কি ,ডিকশনারির মেথডগুলি এবং পাইথনে এটি কে কিভাবে ব্যবহার করব ?
Table of Contents
Definition of Dictionary in Python
ডিকশনারি হল পাইথনের একটি built-in ডেটা স্ট্রাকচার dictionary তে প্রতিটা এলিমেন্টের দুটি করে অংশ থাকে , প্রথমটি হলো key এবং দ্বিতীয়টি হল value। প্রত্যেকটি key এবং value একটি কোলন ( : ) দ্বারা সেপারেট থাকে এবং প্রত্যেকটি এলিমেন্ট কমা ( , ) দ্বারা সেপারেট থাকে ডিকশনারি প্রকাশ করতে পাইথনে কার্লি ব্র্যাকেট { } ব্যবহার করা হয়। উদাহরণ –

mydict={ key1 : value1 , key2 : value2 }চলুন এবার কিছু গুরুত্বপূর্ণ তথ্য জেনে নেওয়া যাক ডিকশনারি সম্পর্কে –
Keys are unique
অর্থাৎ ডিকশনারিতে প্রত্যেকটি key ইউনিক( unique ) হবে অর্থাৎ আমরা একটি ডিকশনারি তে দুটি একই নামের key রাখতে পারব না।যদি দুটি key একই নামের হয় তাহলে যেটা শেষে দেওয়া হবে ওটা ফাইনাল key হিসাবে ধরা হবে।
mydict={"website":"python.org","website":"techinbengali.com"}
print(mydict)
print(type(mydict)){'website': 'techinbengali.com'}
<class 'dict'>Keys are immutable data-type
ডিকশনারি তে প্রত্যেকটি key immutable ডেটা টাইপ অর্থাৎ String , number এবং tuple।
mydict={"website":"techinbengali.com",1:"python",(2,3):['tech','technology']}
print(mydict)
print(type(mydict)){'website': 'techinbengali.com', 1: 'python', (2, 3): ['tech', 'technology']}
<class 'dict'>কিন্তু যদি আমরা key হিসাবে একটি লিস্ট নিই তাহলে আমরা error পাবো। নীচের প্রোগ্রামটি লক্ষ করুন ।
mydict={"website":"techinbengali.com",1:"python",(2,3):['tech','technology'],[1]:[1]}
print(mydict)
print(type(mydict))ERROR!
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<main.py>", line 3, in <module>
TypeError: unhashable type: 'list'Keys are case – sensitive
অর্থাৎ একটি ডিকশনারি তে যদি একই নামের দুটি কি থাকে তাহলে অবশ্যই তাদের দুজনের আলাদা case হতে হবে। এখানে case মানে – uppercase বা lowercase র কথা বলা হয়েছে।
mydict={"name":"tech","Name":"tech2"} # different case
print(mydict)
mydict={"name":"tech","name":"tech2"} # same case
print(mydict){'name': 'tech', 'Name': 'tech2'}
{'name': 'tech2'}Also Read :- What is Set in Python | Learn in Easy Bengali 2024
Creating a Dictionary in Python
আমরা পাইথনে দুই ভাবে ডিকশনারি তৈরি করতে পারি।
Normal way
ডিকশনারি element গুলিকে কার্লি ব্র্যাকেটের { } মধ্যে কমা ( , ) দিয়ে আলাদা করে লেখা হয় এবং প্রতিটা এলিমেন্ট key এবং value দ্বারা তৈরি হয় । আবার key , value গুলি কোলন ( : ) দ্বারা সেপারেট থাকে।
Empty Dictionary in Python
mydict={}
print(mydict)
print(type(mydict)){}
<class 'dict'>Dictionary with key-value pair
mydict={"website":"techinbengali.com","category":"python"}
print(mydict)
print(type(mydict)){'website': 'techinbengali.com', 'category': 'python'}
<class 'dict'>Using dict ( ) function
আমরা ডিকশনারির built-in , dict ( ) ফাংশন ব্যবহার করে একটি ডিকশনারি তৈরি করতে পারি । তবে dict ( ) ফাংশন এর মধ্যে আমাদের এলিমেন্ট গুলি একটা লিস্টের মধ্যে থাকে। এবং সেই লিস্টের মধ্যে প্রতিটি এলিমেন্ট এক একটা tuple হিসেবে চিহ্নিত হয়। সেই টাপেলের 0 নম্বর ইনডেক্স এ key এবং 1 নম্বর ইনডেক্সে value থাকে।
Empty Dictionary in Python
mydict=dict()
print(mydict)
print(type(mydict)){}
<class 'dict'>Dictionary with key-value pair
mydict=dict([("website","techinbengali.com"),("category","python")])
print(mydict)
print(type(mydict)){'website': 'techinbengali.com', 'category': 'python'}
<class 'dict'>Also Read :- What is Tuple in Python in Easy Bengali 2024
Accessing elements in Dictionary in Python
পাইথনের বিল্ট ইন ডেটা স্ট্রাকচার যেমন লিস্ট এবং টাপেল এ ডেটা এক্সেস করার জন্য আমরা ইনডেক্স ব্যবহার করি । কিন্তু , ডিকশনারি তে আমরা কোন ডেটাকে অ্যাকসেস করার জন্য এর key ব্যবহার করে থাকি।
For Known Key
mydict={"website":"techinbengali.com","category":"python"}
print(mydict["category"])pythonFor Unknown Key
কিন্তু যদি আমরা এমন একটি key এর ভ্যালুকে দেখতে চাই , যেই key আমাদের তৈরি করা ডিকশনারির মধ্যে নেই তাহলে পাইথন আমাদেরকে কি KeyError নামে একটা Exception রেইজ করবে।
mydict={"website":"techinbengali.com","category":"python"}
print(mydict["url"])ERROR!
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<main.py>", line 4, in <module>
KeyError: 'url'উপরের ডিকশনারিতে ‘url‘ নামে কোনো key নেই , তাই পাইথন KeyError নামক Error দিয়েছে ।
Adding element in a Dictionary in Python
আমরা যদি ডিকশনারি তে নতুন একটা key – value পেয়ার add করতে চাই তাহলে আমরা নিম্নলিখিত সিনট্যাক্স অনুসরণ করে কাজটি করতে পারব।
Syntax : dictionary_name['key_name'] = valueনিচের উদাহরণটি লক্ষ্য করুন, সেখানে url নামে কোন key নেই কিন্তু আমরা url নামে একটি key তৈরি করলাম এবং সেখানে আমাদের ওয়েবসাইটে url দিলাম অর্থাৎ আমরা mydict নামক একটা ডিকশনারির মধ্যে একটা এলিমেন্টকে key-value পেয়ারে add করলাম এবং সর্বশেষ সেই ডিকশনারিটি প্রিন্ট করালাম।
Example
mydict={"website":"techinbengali.com","category":"python"}
mydict["url"]="https://techinbengali.com/"
print(mydict){'website': 'techinbengali.com', 'category': 'python', 'url': 'https://techinbengali.com/'}Updating value in a Dictionary in Python
আমরা যদি ডিকশনারির কোন একটি key এর value পরিবর্তন (update ) করতে চাই তাহলে আমরা নিম্নলিখিত সিনট্যাক্স অনুসরণ করে কাজটি করতে পারব।
Syntax : dictionary_name['key_name'] = updated_valueনিচের উদাহরণটি লক্ষ্য করুন, সেখানে url নামে একটা কি আমাদের ডিকশনারি তে আছে , এখন আমরা url এই key এর value টাকে চেঞ্জ করে python.org করলাম এবং সর্বশেষে সেই ডিকশনারিটি প্রিন্ট করালাম।
Example
mydict={'website': 'techinbengali.com', 'category': 'python', 'url': 'https://techinbengali.com/'}
mydict["url"]="https://www.python.org/"
print(mydict){'website': 'techinbengali.com', 'category': 'python', 'url': 'https://www.python.org/'}Deleting Element from a Dictionary in Python
আমরা নিম্নলিখিত সিনট্যাক্স অনুসরণ করে আমরা ডিকশনারি থেকে একটা item কে ডিলিট করতে পারি।
Syntax : del dictionary_name['key_name']নিচের উদাহরণটি লক্ষ্য করুন, সেখানে আমরা category নামক key তাকে আমাদের mydict নামক ডিকশনারি থেকে ডিলিট করেছি। এবং সর্বশেষে সেই ডিকশনারিটি প্রিন্ট করে দেখলাম আমাদের mydict নামক ডিকশনারি তে category নামক কোন key নেই অর্থাৎ key টি সাকসেসফুলি ডিলিট হয়েছে।
Example
mydict={'website': 'techinbengali.com', 'category': 'python', 'url': 'https://techinbengali.com/'}
del mydict['category']
print(mydict){'website': 'techinbengali.com', 'url': 'https://techinbengali.com/'}এছাড়াও আরো অনেক ভাবে ডিকশনারি থেকে আইটেম ডিলিট করা যায় যেগুলি আমরা এই পোস্টের ডিকশনারি মেথড এ আলোচনা করব।
Looping over Dictionary in Python
আমরা for লুপ ব্যবহার করে বিভিন্ন পদ্ধতিতে ডিকশনারির প্রত্যেকটি আইটেম দেখতে পারি।
Getting key by using normal For loop
আমরা for loop ব্যবহার করে আমাদের তৈরি করা ডিকশনারি থেকে শুধুমাত্র key গুলিকেই এক্সেস করতে পারব কোন ভ্যালু পাবনা তবে ভ্যালু পেতে গেলে আমাদের জানতে হবে, কিভাবে আমরা key থেকে ডিকশনারির value কে এক্সেস করতে পারি। যেটা আমরা উপরে আলোচনা করেছি।
Example
mydict={'website': 'techinbengali.com', 'category': 'python', 'url': 'https://techinbengali.com/'}
for key in mydict:
print(f"key: {key} -> value: {mydict[key]}")Output
key: website -> value: techinbengali.com
key: category -> value: python
key: url -> value: https://techinbengali.com/Getting key and value by using items( ) methods
নিচের উদাহরণটি লক্ষ্য করুন, আমরা কিভাবে items( ) মেথড ব্যবহার করে একটি ডিকশনারি থেকে key এবং value দুটোকেই অ্যাক্সেস করছি।
Example
mydict={'website': 'techinbengali.com', 'category': 'python', 'url': 'https://techinbengali.com/'}
for key,value in mydict.items():
print(f"key: {key} -> value: {value}")Output
key: website -> value: techinbengali.com
key: category -> value: python
key: url -> value: https://techinbengali.com/অর্থাৎ mydict.items( ) মেথডটি আমাদেরকে ডিকশনারির key এবং value কে একটা টাপেল আকারে রিটার্ন করছে এবং সেটিকে আমরা দুটি আলাদা ভ্যারিয়েবল key এবং value মধ্যে স্টোর করছি। এবং সেটিকে আমাদের প্রয়োজন মতন ব্যবহার করছি , এখানে ভ্যালুগুলিকে প্রিন্ট করছি।
Also Read :- What are Data Structures in Python in Easy Bengali 2024
Nested Dictionaries in Python
আমরা একটি ডিকশনারির মধ্যে আরও ডিকশনারিকে রাখতে পারি।
Example
students={
"BBA":{"Total_student":150,"Room_no":201,"HOD":"xyz.banarjee"},
"BCA":{"Total_student":150,"Room_no":401,"HOD":"abc.sen"},
"MCA":{"Total_student":60,"Room_no":301,"HOD":"xyz.das"}
}
for key,value in students.items():
print(f"{key} -> {value}")Output
BBA -> {'Total_student': 150, 'Room_no': 201, 'HOD': 'xyz.banarjee'}
BCA -> {'Total_student': 150, 'Room_no': 401, 'HOD': 'abc.sen'}
MCA -> {'Total_student': 60, 'Room_no': 301, 'HOD': 'xyz.das'}Exercise – 1 : how many times each character appears in a string and stores the counts in a dictionary.
Solution
# ----------------------- Level : Beginner ------------------
string="madam"
mydict=dict()
for item in string:
if item not in mydict:
mydict[item]=1
else:
mydict[item]+=1
print(mydict)OR
# ----------------------- Level : Intermediate ------------------
string="madam"
mydict=dict()
for item in string:
mydict[item]=string.count(item)
print(mydict)OR
# ----------------------- Level : Expert ------------------
string="madam"
mydict={item:string.count(item) for item in string}
print(mydict)Output
{'m': 2, 'a': 2, 'd': 1}Also Read :- Basic List Operations and List methods in Easy Bengali 2024
Basic Dictionary Operations in Python (বেসিক ডিকশনারি অপারেশন)
len ( )
একটি ডিকশনারির length বা দৈর্ঘ্য রিটার্ন করে।অর্থাৎ ডিক্শনারিতে কতগুলি key আছে।
Example
mydict={'m': 2, 'a': 2, 'd': 1}
print(len(mydict))Output
3Membership ( in )
এটি দিয়ে আমরা দেখতে পারি একটি key ডিকশনারির এর মধ্যে আছে কি না ? যদি থাকে True রিটার্ন করবে যদি না থাকে False রিটার্ন করবে।
Example
mydict={'m': 2, 'a': 2, 'd': 1}
print('m' in mydict)
print('s' in mydict)Output
True
FalseMembership ( not in )
এটি দিয়ে আমরা দেখতে পারি একটি key ডিকশনারির এর মধ্যে আছে কি না ? যদিও এটির ব্যবহার in এর ঠিক উল্টো (opposite)। যদি না থাকে True রিটার্ন করবে যদি থাকে False রিটার্ন করবে।
Example
mydict={'m': 2, 'a': 2, 'd': 1}
print('m' not in mydict)
print('s' not in mydict)Output
False
Truemax ( )
একটি ডিকশনারির মধ্যে থেকে বড়ো (maximum) key রিটার্ন করবে।
Example
mydict={'m': 2, 'a': 2, 'd': 1}
print(max(mydict))Output
mmin ( )
একটি সেটের মধ্যে থেকে ছোট (minimum) key রিটার্ন করবে।
Example
mydict={'m': 2, 'a': 2, 'd': 1}
print(min(mydict))Output
astr ( )
পুরো ডিক্শনারিটি একটি string আকারে রিটার্ন করবে।
Example
mydict={'m': 2, 'a': 2, 'd': 1}
print(str(mydict))
print(type(str(mydict)))Output
{'m': 2, 'a': 2, 'd': 1}
<class 'str'>
Also Read :- What is List in Python | Learn in Easy Bengali 2024
Basic Dictionary Methods in Python (বেসিক ডিকশনারি মেথডস )
Clear ( )
এই মেথডের সাহায্য ডিকশনারি থেকে সমস্ত entry কে ডিলিট করা যায়।
Example
mydict={'m': 2, 'a': 2, 'd': 1}
mydict.clear()
print(mydict)Output
{ }Copy ( )
এই মেথডটি একটি ডিকশনারী shallow কপি রিটার্ন করে।
Example
mydict={"website":"techinbengali.com","url":"https://techinbengali.com/"}
mydict2=mydict.copy()
mydict2['url']="https://www.python.org/"
print("actual dictionary mydict : ",mydict)
print("after modification in mydict2 : ",mydict2)Output
actual dictionary mydict : {'website': 'techinbengali.com', 'url': 'https://techinbengali.com/'}
after modification in mydict2 : {'website': 'techinbengali.com', 'url': 'https://www.python.org/'}get ( key )
এই মেথডে আমরা key হিসাবে যে আরগুমেন্ট পাস করব তার ভ্যালু রিটার্ন করবে।
Example
mydict={"website":"techinbengali.com","url":"https://techinbengali.com/"}
print(mydict.get('website'))Output
techinbengali.comfromkeys ( sequence [ , value ] )
একটা সিকুয়েন্স থেকে, নতুন ডিকশনারি তৈরি করবে key এর সাথে এবং ভ্যালুতে যা পাঠাবো সেটা প্রত্যেকটি key এর একই ভ্যালুই হবে। যদি আমরা কোন ভ্যালু না পাঠাই , তাহলে ডিফল্ট ভ্যালু হিসেবে None assign হবে।
Example
list=['website','url','category']
mydict=dict.fromkeys(list,'xxxxxxxx') # without default value
print(mydict)
mydict=dict.fromkeys(list) # with default value (None is assigned)
print(mydict)Output
{'website': 'xxxxxxxx', 'url': 'xxxxxxxx', 'category': 'xxxxxxxx'}
{'website': None, 'url': None, 'category': None}items ( )
এই মেথডটি একটা টাপেলের (key – value পেয়ার) লিস্ট রিটার্ন করবে।
Example
mydict={"website":"techinbengali.com","url":"https://techinbengali.com/"}
print(mydict.items())Output
dict_items([('website', 'techinbengali.com'), ('url', 'https://techinbengali.com/')])keys ( )
এই মেথডটি dictionary সমস্ত key গুলিকে লিস্ট ফরম্যাট এ রিটার্ন করবে।
Example
mydict={"website":"techinbengali.com","url":"https://techinbengali.com/"}
print(mydict.keys())Output
dict_keys(['website', 'url'])values ( )
এই মেথডটি dictionary সমস্ত value গুলিকে লিস্ট ফরম্যাট এ রিটার্ন করবে।
Example
mydict={"website":"techinbengali.com","url":"https://techinbengali.com/"}
print(mydict.values())Output
dict_values(['techinbengali.com', 'https://techinbengali.com/'])update ( dictionary_2 )
এই মেথডটির সাহায্যের দুটি ডিকশনারি কে add করা যায়।
Example
mydict={"website":"techinbengali.com","url":"https://techinbengali.com/"}
mydict2={"category":['python','technology']}
mydict.update(mydict2)
print(mydict)Output
{'website': 'techinbengali.com', 'url': 'https://techinbengali.com/', 'category': ['python', 'technology']}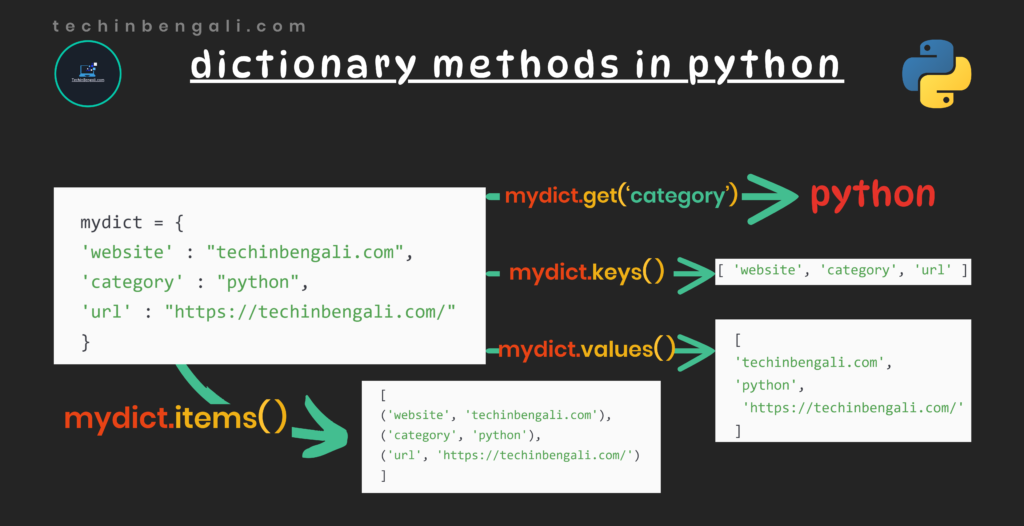
Also Read :- What is Module in Python | Learn in Easy Bengali 2024
Difference Between Set and Dictionary in python
| set | dictionary |
| সেট হলো mutable যদিও , সেটের সকল এলিমেন্টকে add, delete এবং read করা যায় , কিন্তু আপডেট করা যায় না । | ডিকশনারি হলো mutable কারণ ডিকশনারির সকল এলিমেন্টকে add, update , delete এবং read করা যায়। |
| সেটে ডুপ্লিকেট এলিমেন্ট allow নয়। | ডিকশনারিতে ডুপ্লিকেট ভ্যালু allow , কিন্তু ডুপ্লিকেট key allow নয়। |
| সেটে শুধুমাত্র immutable ডেটাটাইপ allow। | ডিকশনারিতে key গুলি শুধুমাত্র immutable ডেটাটাইপ কিন্তু, ভ্যালুগুলি immutable এবং mutable ডেটাটাইপ হতে পারে। |
| সেটের এলিমেন্টগুলিকে access করার জন্যে কোনো রকম index এর দরকার নেই। | ডিকশনারিতে এলিমেন্টগুলিকে access করার জন্যে আমাদের key টাকে ইনডেক্স হিসাবে ব্যাবহার করা হয়। |
| সেট একটি unordered ডেটাস্ট্রাকচার। | ডিকশনারি একটি ordered ডেটাস্ট্রাকচার। |
এই পোস্টটি পড়ে আপনাদের মূলবান মতামত জানাতে আমাদের কমেন্ট করুন। আপনাদের কোনো প্রশ্ন থাকলে নির্দ্ধিধায় জিজ্ঞেসা করুন। আমরা চেষ্টা করবো যতো দ্রুত সম্ভব উত্তর দেবার।
ধন্যবাদ!!



